PREBIOTICS v. FIBRE
Dietary fibre, also known as roughage or bulk, is found in plant-based foods which our bodies cannot digest or absorb. Instead of being broken down and absorbed like other nutrients, fibre passes relatively intact through the stomach, small intestine, and colon, providing a range of health benefits.Along with adequate fluid intakes, fibre is responsible for quickly moving foods through the digestive tract, helping it function optimally. Fibre works by drawing fluids from the body to add bulk to the stool.
Including an adequate amount of dietary fibre in your diet is crucial for maintaining good digestive health, preventing constipation, and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and certain types of cancer. According to research, over 90% adults in the UK eat less than the recommended minimum of 30 grams of fibre per day with the average for most being under 20 g of fibre.
Soluble and insoluble fibre
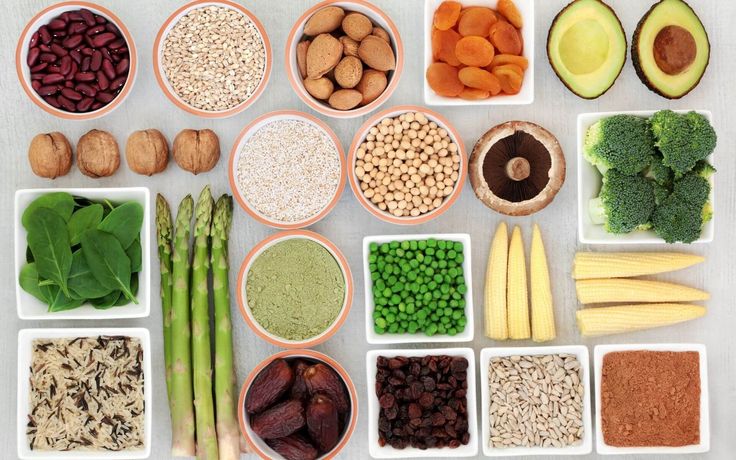
Soluble fibre dissolves in water to form a gel-like consistency. It can help lower cholesterol levels, regulate blood sugar levels, and promote a feeling of fullness or satiety. Good sources of soluble fibre include oats, chia seeds, linseeds (flax), nuts, split peas, lentils, quinoa and bananas. Psyllium husk is an excellent type of soluble fibre, commonly used as a dietary supplement to promote digestive health due to its ability to increase stool bulk and promote regular bowel movements. Psyllium husk can help with constipation, diarrhoea, and other gastrointestinal issues. Additionally, it may help lower cholesterol levels and improve heart health. Insoluble fibre does not dissolve in water and adds bulk to the stool, helping to promote regular bowel movements and prevent constipation. It can also help maintain healthy digestive function. Whole grains, wheat bran, nuts, and many vegetables are good sources of insoluble fibre.
PREBIOTICS
Prebiotics or prebiotic fibre, are a type of non-digestible fibre that serves as an important source of food for the beneficial bacteria living in your gut. Prebiotics are essentially a form of dietary fibre that ‘feeds’ and supports the probiotics already present in your gut. Consuming prebiotics can help promote the growth and activity of beneficial bacteria, such as Lactobacilli and Bifidobacteria, in your digestive system. This, in turn, helps to maintain a healthy balance of gut flora and supports various aspects of your health, including digestion, immune function, and nutrient absorption.
Common food sources of prebiotics include: chicory root, jerusalem artichokes, onions, garlic, leeks, asparagus and bananas. Inulin is an excellent prebiotic fibre available in capsule and powder form. It’s a versatile ingredient, suitable for adding to drinks or for baking as it can preserve moisture and act as a binding agent, whilst providing a slighty sweet taste.
PROBIOTICS
Probiotics are a type of organism or ‘live bacteria’ which can help boost the amount of beneficial bacteria in your gut. Nestled inside your gut are trillions of these live microorganisms that make up the microbiome. They are also found in supplements, fermented foods (such as kimchi, tempeh and miso) and probiotic drinks, such as kombucha and kefir.
Different microbes living in your gastrointestinal tract play a role in either promoting health or disease. For example, many of these bacterial cells are considered “good bacteria” and help support immune function, enhance nutrient absorption, and aid in the synthesis of key neurotransmitters and other compounds.